Optimize Facilities with CMMS Software
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) centralizes maintenance data, automates scheduling, and enforces consistent workflows to reduce downtime and improve asset ROI. This article explains what CMMS software is, how its core modules work together, and why facilities managers and property teams adopt these tools to move from reactive repairs to planned, measurable maintenance. Readers will learn core CMMS features, the top business benefits including cost and compliance improvements, practical preventive maintenance scheduling tips, and tactics for efficient work order and asset management. The guide synthesizes current research and industry best practices to show concrete steps facilities teams can take to improve uptime, extend equipment life, and optimize parts inventory. Each H2 section includes brief implementation guidance and data-focused tables to make comparisons actionable for facility leaders evaluating building maintenance software and asset tracking solutions.
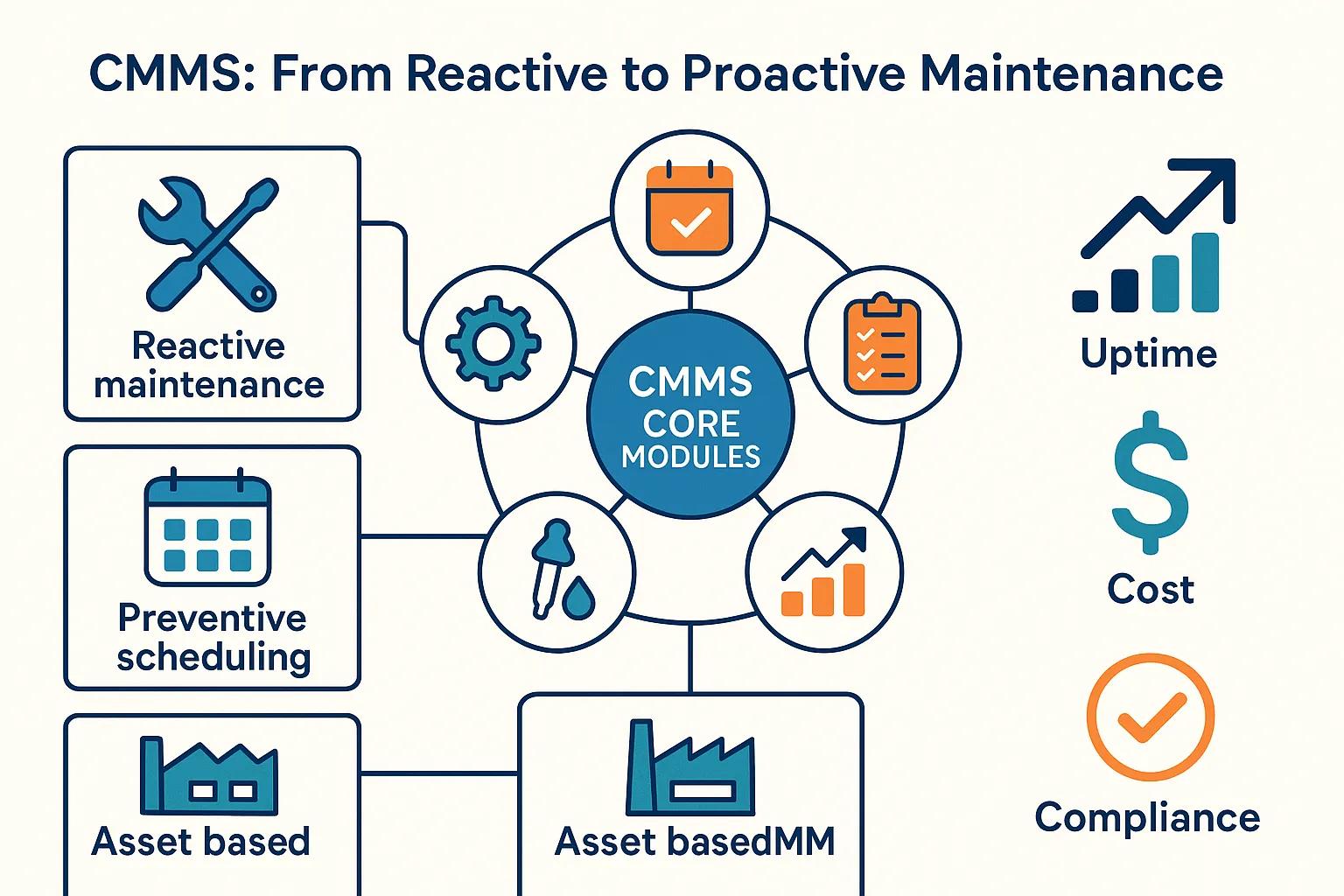
What Is CMMS Software and How Does It Improve Facilities Management?
CMMS software is maintenance software that organizes work orders, preventive maintenance scheduling, asset registries, inventory, and reporting into a single platform to improve operational visibility and reduce manual effort. By centralizing records and automating schedules, CMMS reduces human error, accelerates response times, and creates auditable histories that support compliance and better capital planning. The result is higher uptime, fewer emergency repairs, and clearer KPIs for maintenance teams. Below are the core features that define modern CMMS platforms and how each contributes to streamlined facilities management.
Defining CMMS and Its Core Features for Facilities Management
CMMS core modules include work order management, preventive maintenance scheduling, an asset registry, parts and inventory control, and reporting/analytics that together form the maintenance backbone. Work order modules capture requests, assign tasks, and track completion; preventive maintenance modules schedule recurring tasks based on time or usage; asset registries link maintenance histories to specific equipment; inventory modules manage spare parts levels and reorder points; analytics provide KPIs like MTTR and uptime. These components form an integrated workflow where an asset record triggers PMs, which generate work orders and consume inventory while producing compliance-ready reports.
How CMMS Software Streamlines Maintenance Operations
CMMS streamlines operations through automated scheduling, condition or sensor-based triggers, mobile access for field technicians, and workflow routing that ensures the right team gets the right job at the right time. For example, an IoT alert can create a work order, dispatch a technician with a mobile checklist, and update the asset history automatically when the job is closed. Centralized data reduces duplicated tasks and accelerates troubleshooting by surfacing prior repairs and parts used. That operational transparency enables continuous improvement and helps facilities plan preventive budgets rather than chasing unplanned breakdowns.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using CMMS Software for Facilities?
CMMS adoption delivers measurable improvements in cost control, uptime, compliance, and productivity by converting maintenance into a predictable operational function. Centralized scheduling and inventory control lower emergency procurement and overtime expenses, while historical data enables better lifecycle decisions and reporting for regulators or auditors. Implementers commonly see improvements in mean time between failures, reduced MTTR, and clearer visibility into parts consumption and labor efficiency.
Different maintenance approaches yield distinct operational outcomes and cost profiles.
| Approach | Characteristic | Typical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive maintenance | Unplanned repairs, ad-hoc parts buying | Higher downtime, higher emergency costs |
| Preventive scheduling | Time- or usage-based tasks | Reduced failures, improved uptime |
| Asset-centric CMMS | Linked asset histories and PMs | Improved lifecycle decisions, CAPEX planning |
This comparison shows that moving from reactive to preventive, asset-aware maintenance produces clearer cost savings and operational stability, which supports strategic facility investment decisions.
How Does CMMS Reduce Maintenance Costs and Downtime?
Shifting work from reactive to scheduled preventive maintenance lowers emergency parts procurement and reduces overtime by planning labor and stocking critical spares. Clear work orders and mobile access shorten diagnosis time and reduce mean time to repair (MTTR), while inventory management avoids disruptive shortages. Data from implementations often reveal a measurable drop in unplanned downtime and a reduction in spare-parts carrying costs when reorder points and usage rates are optimized.
The table below summarizes how preventive practices map to common benefits for facilities stakeholders.
| Preventive Practice | Attribute | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduled PMs | Frequency-driven tasks | Fewer emergency repairs |
| Inventory optimization | Reorder point + min/max | Lower procurement cost |
| Detailed work orders | Standardized instructions | Faster MTTR |
These attributes show how routine PMs and disciplined inventory reduce both downtime and reactive spending, enabling facilities teams to reallocate resources to higher-impact projects.
In What Ways Does CMMS Enhance Asset Performance and Compliance?
A CMMS enhances asset performance by maintaining complete lifecycle histories, automating inspection and compliance schedules, and producing reports required for audits or regulatory reviews. Asset records with identifiers, location data, and maintenance logs let managers identify patterns, prioritize replacements, and extend useful life through targeted interventions. Automated compliance checklists and audit trails reduce administrative burden and provide evidence for inspections. Together, these capabilities support data-driven decisions about repair versus replace and help facilities meet safety and regulatory obligations consistently.
After reviewing these benefit-driven outcomes, many organizations look for implementation partners who understand both facilities operations and growth objectives. RevUp Now positions itself as a growth-focused partner for service-based businesses, helping teams translate CMMS benefits into scalable processes through automation and tailored workflows.
Their approach emphasizes aligning maintenance automation with business growth goals so that CMMS adoption not only improves uptime and cost control but also supports long-term operational scaling.
How Can Preventive Maintenance Scheduling Optimize Facility Operations?
Preventive maintenance (PM) scheduling aligns inspections and routine tasks with asset usage and risk profiles to prevent wear-related failures and optimize resource allocation. Effective PM uses a mix of time-based, usage-based, and condition-based triggers to prioritize work and avoid unnecessary interventions. When schedules are data-driven, teams can plan labor, manage parts, and measure effectiveness using KPIs like scheduled vs completed ratio and failure reduction. The following best practices help facilities launch and scale an effective PM program.
Key best practices establish a practical PM foundation and measurable roll-out criteria.
- Inventory critical assets: Begin with assets whose failure impacts operations most.
- Define clear tasks: Create concise PM procedures and required parts lists.
- Use prioritized scheduling: Rank PMs by risk and impact to optimize resources.
These steps form a phased approach from inventory and task definition to prioritized scheduling, making PM efforts measurable and manageable during rollout.
| Asset Class | Recommended Frequency | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC critical units | Quarterly or runtime-based | Fewer emergency outages |
| Backup generators | Monthly inspections | Improved reliability during outages |
| Production pumps | Usage-hour based | Reduced mechanical wear |
Linking these PM frequencies to outcomes helps teams forecast spare parts and labor needs and quantify failure reductions over time.
What Are Best Practices for Implementing Preventive Maintenance?
Begin PM implementation by documenting critical assets, standardizing task instructions, and setting realistic initial frequencies that you can measure and adjust. Track KPIs such as percentage of scheduled tasks completed, reduction in emergency work orders, and MTTR to judge effectiveness and refine schedules. Start small with high-impact assets and expand the program as data validates frequency and task lists. Regularly review PM results to transition marginal tasks to condition-based strategies when monitoring data supports it.
Modern PM programs benefit from automation and AI-enhanced scheduling that optimize task timing based on usage patterns and sensor inputs. Integrating smart automation reduces manual scheduling overhead and helps prioritize work that yields the highest uptime improvement while reducing unnecessary maintenance.
How Does Preventive Maintenance Software Reduce Equipment Failures?
Preventive maintenance software enforces consistent execution of tasks, keeps detailed histories for root-cause analysis, and supports condition-based triggers that preempt failures. Historical records reveal recurring faults and inform task adjustments or part replacements that prevent repeat breakdowns. Condition monitoring and predictive alerts based on operational thresholds can escalate issues before they become catastrophic, shifting the maintenance model from reactive to anticipatory. By combining scheduled PMs with data-driven condition checks, facilities teams reduce unexpected downtime and extend asset life.
How Does Work Order and Asset Management Improve Facility Efficiency?
Work order and asset management connect requests, assignments, and asset context so technicians arrive prepared and complete jobs faster, which increases first-time-fix rates and reduces revisit requirements. Asset-linked orders ensure parts and history are visible during assignment, and SLA-driven prioritization channels resources to the most impactful tasks. Reporting on assignment times, response rates, and closure quality drives continuous improvement and helps management allocate budget to maintenance activities that reduce recurring failures. Below are concrete strategies for work order intake and asset tracking that improve operational efficiency.
Practical strategies standardize intake and prioritization while equipping field teams for rapid resolution.
- Standardize request intake: Use categories and templates to reduce triage time.
- Apply SLA rules: Route urgent vs routine work automatically based on impact.
- Equip technicians with mobiles: Provide checklists, drawings, and parts lists on-site.
Implementing these strategies reduces administrative friction and accelerates technician productivity, creating measurable efficiency gains across the maintenance function.
| Management Function | Attribute | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Work order routing | Priority + SLA | Faster response times |
| Asset-linked work orders | Contextual history | Higher first-time fix rate |
| Inventory tie-in | Automatic parts allocation | Lower MTTR and fewer delays |
These mappings show how pairing disciplined work order rules with asset context and inventory integration shortens repair cycles and supports predictable operations.
What Are Effective Strategies for Work Order Management?
Effective work order management standardizes intake forms, enforces classification rules to expedite prioritization, and uses SLAs to route tasks to the right teams automatically. Technicians should receive clear checklists and required parts lists via mobile CMMS apps to reduce return trips. Regularly review closed work orders to spot process improvements and update templates to capture the right diagnostic data. This disciplined approach reduces administrative overhead, improves response consistency, and provides data to refine staffing and spare-parts strategies.
Customized automation and tailored systems further streamline dispatching and prioritization for growing service teams. RevUp Now helps service-based organizations design CMMS workflows and automation rules that scale with business needs, ensuring work order routing, prioritization, and mobile enablement match operational growth targets.
How Does Asset Tracking Extend Equipment Lifespan?
Asset tracking combines unique identifiers, location data, maintenance histories, and condition records to enable targeted interventions that extend equipment life and reduce premature replacements. By mapping service intervals to actual usage and condition trends, teams can schedule timely repairs or component replacements that prevent cascading failures. Tracking also informs CAPEX planning by revealing which assets are repairable versus those that require replacement based on lifecycle costs. Metrics to monitor include uptime, lifecycle cost per year, and failure frequency to guide replacement strategies grounded in operational data.
Conclusion
Implementing CMMS software significantly enhances facilities management by streamlining maintenance operations, reducing costs, and improving asset performance. By centralizing data and automating workflows, organizations can transition from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, ultimately leading to increased uptime and compliance. To experience these transformative benefits, consider exploring tailored CMMS solutions that align with your operational goals. Start optimizing your facility’s maintenance processes today for a more efficient and cost-effective future.








